- Internal environment of a business includes all of the following except
(A) Company culture
(B) Customers
(C) Patents and trade secrets
(D) Company image - Balance of payment includes components:
(A) Current Account, Capital Account, Unilateral Payments Account, Official Settlement Accounts
(B) Revenue Account, P&L A/c, Capital Account, Official Account
(C) Trade Account, Activity Account, Revenue Account and Currency Account
(D) Forex Account, Trade Account, Funds Accounts - Which one is the main objective of fiscal policy in India?
(A) To increase liquidity in the economy
(B) To promote price stability
(C) To minimise the inequalities of income and wealth
(D) To promote employment opportunities - Statement (A) : In the context of globalisation, the most important challange facing India is to boost exports.
Reason (R) : It may increase the country’s growth rate.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the incorrect explanation of (A)
(C) (A) is true but (R) is false
(D) (A) is false but (R) is true - Possible impact of WTO on various aspects of the Indian economy:
(i) Quantitative restriction will be allowed
(ii) Second hand cars will be imported
(iii) There will be dumping of Chinese goods
(iv) Increase in population
(v) Child labour exploitation
(vi) Unemployment will increase Which combination is appropriate?
(A) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(B) (iii), (iv) and (v)
(C) (ii), (iii) and (vi)
(D) (iv), (v) and (vi) - Which of the following factors is an obstacle to globalisation?
(A) Government policy and regulation
(B) Niche markets
(C) Human Resources
(D) Competition - Balance of payment can be made favourable if
(A) Exports are increased.
(B) Imports are increased.
(C) Devaluation of money.
(D) Both (A) and (C) - Which Indian city has been chosen by the World Bank for setting up its back office operations?
(A) Bangalore
(B) Kolkata
(C) Chennai
(D) New Delhi - The Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) of the WTO says that farm subsidies cannot be more than 10 per cent of the
(A) Gross Domestic Product of a country.
(B) Value of agricultural production.
(C) National Income of a country.
(D) Value of agricultural exports. - South-South Cooperation means
(A) Increasing diplomatic relation among emerging economies.
(B) The flow of resources from one developing country to another.
(C) Increasing investment between developing countries.
(D) Rising trade between the countries. - In reference to the accounting standards, choose the correct statement:
(A) Accounting standards codify the generally accepted accounting principles.
(B) They lay down the norms of accounting policies and practices by way of codes or guidelines.
(C) The main purpose of accounting standards is to provide information to the user as to the basis on which the accounts have been prepared.
(D) All of the above - Triple bottom line accounting is also called
(A) Incremental Costing.
(B) Management Accounting.
(C) Full Cost Accounting.
(D) Historical Cost Accounting. - Amalgamate Adjustment Account is opened in the books of transferee company to incorporate _______ in case of merger.
(A) The assets of the transferor company
(B) The statutory reserves of the transferor company
(C) The liabilities of the transferor company
(D) The non-statutory reserves of the transferor company - In case of other enterprises (other than financial enterprises) cash flow arising from interest paid should be classified as cash flow from _______ while dividends
and interest received should be stated as cash flow from _______.
(A) Operating activities, Financing activities
(B) Financing activities, Investing activities
(C) Financing activities, Financing activities
(D) Investing activities, Operating activities - Which of the following are the assumptions of marginal costing?
(a) All the elements of cost can be divided into fixed and variable components.
(b) Total fixed cost remains constant at all levels of output.
(c) Total variable cost varies in proportion to the volume of output.
(d) Per unit selling price remains unchanged at all levels of operating activity.
(A) (a) and (b)
(B) (b) and (c)
(C) (a) and (d)
(D) All of (a), (b), (c) and (d) - XYZ Ltd. has a Debt-Equity ratio of 1·6 compared to the industry average of 1·4. This means that the company
(A) Will be viewed as having creditworthiness.
(B) Has greater than average financial risk when compared to other firms in the industry.
(C) Has less liquidity than other firms in the industry.
(D) Will not experience any difficulty with its creditors. - In September, 2019, actual materials used amounted to 5650 kg., budgeted output was 1000 units and standard materials usage was 5 kg. per unit. Actual output was 1075 units. If the standard material cost of each product is Rs.25, the material usage variance will be
(A) Rs. 1,375 Favourable
(B) Rs.3,250 Favourable
(C) Rs.6,875 Adverse
(D) Rs.1,375 Adverse - The auditor has noticed existence of recurring losses on sale of fixed assets. This indicates that
(A) depreciation charges are insufficient.
(B) policy of sale or disposal of fixed assets needs to be reviewed.
(C) the sale of assets have not been properly authorised.
(D) there are accounting errors. - While verifying intangible assets, an auditor would recompute amortisation charges and determine whether mortisation period is reasonable. The auditor actually tries to establish _______ by doing it.
(A) Disclosure
(B) Existence
(C) Valuation
(D) Possession - Which sampling method is used when the likelihood of finding evidence by an auditor is low?
(A) Random
(B) Systematic
(C) Cluster
(D) Discovery - The concept of cardinal utility in economics was introduced by
(A) A. Marshall
(B) J. Hicks
(C) P. A. Samuelson
(D) J. M. Keynes - A consumer will attain equilibrium in terms of the indifference curve analysis when(A) The budget line is tangent to the indifference curve.
(B) The indifference curve has a positive slope.
(C) The indifference curve has a negative slope.
(D) The budget line is tangent to the indifference curve and the indifference curve is convex to the origin. - Price _______ when there is excess market demand over market supply.
(A) tends to increase
(B) tends to decrease
(C) remains constant
(D) can not be determined - If price elasticity of supply is zero, the supply curve will be
(A) A horizontal straight line.
(B) A vertical straight line.
(C) A downward falling straight line.
(D) An upward rising straight line. - The relation between average cost and marginal cost is that
(A) they are parallel to each other.
(B) they are perpendicular to each other.
(C) they have a common point.
(D) they are tangent to each other. - A firm enjoys abnormal profit when
(A) average cost equals price.
(B) average cost is greater than price.
(C) average cost is less than price.
(D) average cost is equal to marginal cost. - The concept of “dead-weight loss” is relevant only under
(A) Monopolistically competitive market.
(B) Perfectly competitive market.
(C) Oligopoly market.
(D) Monopoly market. 
- The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly was introduced by
(A) Samuelson
(B) Chamberlin
(C) Joan Robinson
(D) Sweezy - Marginal revenue will be zero when
(A) ep<1
(B) ep >1
(C) ep=0
(D) ep =1 - Match the items of List-I with those of List-II and indicate the correct code:
List-I List-II (a) Acid Test Ratio (i) Profitability analysis (b) Return on Investment (ii) Activity analysis (c) Debt Equity Ratio (iii) Liquidity analysis (d) Inventory Turnover (iv) Long-term solvency Ratio analysis Codes:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(A) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
(B) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i)
(C) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
(D) (iii) (i) (iv) (ii) - Assertion (A) : The primary motive of a company in using financial leverage is to magnify shareholders’ return under favourable economic conditions.
Reason (R) : To magnify shareholders’ return fixed charged funds can be obtained at a cost higher than the firm’s rate of return on net assets.
Codes:
(A) (R) is correct but (A) is wrong
(B) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
(C) (A) is correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(D) Both (A) and (R) are wrong - Debt financing is a cheaper source of finance because of
(A) Time value of money.
(B) Rate of interest.
(C) Tax deductibility of interest.
(D) Dividends are not payable to lenders. - Lease which includes a third party (a lender) is known as
(A) Operating Lease
(B) Sale and Lease-back
(C) Leveraged Lease
(D) Cross-border Lease - Which one of the following equals the present value of cash outflows and the present value of expected cash inflow from a project?
(A) Net Present Value
(B) Internal Rate of Return
(C) Pay Back Period
(D) Accounting Rate of Return - Operating leverage and Financial leverage of a firm are 3 and 2 respectively. If sales increase by 5%, then earnings before tax will rise by
(A) 15%
(B) 10%
(C) 30%
(D) 25% - Match the items of List-I with those of List-II and indicate the correct code:
List-I List-II (a) Net Income Approach (i) Working Capital Management (b) Profitability Index (ii) Over-Capitalization (c) Concentration (iii) Capital Structure Banking Planning (d) Lower Rate of Return (iv) Capital Budgeting Decision Codes:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(A) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
(B) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(C) (iv) (ii) (iii) (i)
(D) (ii) (iii) (i) (iv) - To maintain international liquidity the Smithsonian Agreement was inked on December 18, 1971 by a group of countries known as
(A) Group of Eight.
(B) Group of Twenty.
(C) Group of Ten.
(D) Group of Forty-four. - Which one of the following is not a method of calculating cost of equity capital?
(A) Dividend-Growth Model
(B) Capital Asset Pricing Model
(C) Yield to Maturity Method
(D) Earning Price Approach - In Covered interest arbitrage
(A) Foreign exchange risk is covered.
(B) Interest fluctuation is covered.
(C) Cross country fluctuation in capital movement is covered.
(D) Interest differential is eleminated. - The arithmetic mean is called the best measure of central tendency because
(A) its value depends on all observations.
(B) it has some algebraic properties.
(C) sampling fluctuation for such a measure is the least.
(D) it is unambiguously defined. - For comparing the variability of two or more distributions we generally use
(A) Range
(B) Mean absolute deviation
(C) Coefficient of variation
(D) Standard Deviation - In the equation y = a + bx, the variable x is called a (an) ________ variable
(A) Dependent
(B) Independent
(C) Dummy
(D) Exogenous - If the correlation coefficient between two variables is –1, we have
(A) one regression line with positive slope.
(B) one regression line with negative slope.
(C) two regression lines each with positive slope.
(D) two regression lines each with negative slope. - The regression coefficient of x on y is 3·1 and that of y on x is 0·9.
(A) This is a correct statement.
(B) This is an incorrect statement.
(C) Nothing can be inferred from such a statement.
(D) More information is necessary. - Report of the World Bank is a source of
(A) Primary data
(B) Secondary data
(C) Observation data
(D) Schedule data - If we throw a dice once the probability of getting an odd number is
(A) 1/6
(B) 1/4
(C) 5/6
(D) 1/2 - Total area under the standard normal curve is
(A) 0
(B) –1
(C) +1
(D) +0·5 - Non-sampling error is present
(A) only in sampling.
(B) only in population.
(C) in both sampling and population.
(D) neither in sampling nor in population. - _______ is an example of probabilistic sampling.
(A) Convenience sampling
(B) Purposive sampling
(C) Simple random sampling
(D) Quota sampling - Communication barriers arising from the inappropriate choice of ‘words’ or ‘phrases’ are known as
(A) Personal barriers
(B) Organisational barriers
(C) Semantic barriers
(D) Psychological barriers - Which of the following is not among Henri Fayols’Fourteen Principles of Management?
(A) Order
(B) Balance
(C) Discipline
(D) Equity - Which of the following terms refers to a summary of the required qualifications, experience and other human qualities to be possessed by a candidate for being eligible to apply for a job?
(A) Job Description
(B) Job Evaluation
(C) Job Specification
(D) Job Design - Which of the following is not a perspective of the Balance Scorecard developed by Kaplan and Norton?
(A) Human Resources
(B) Financial Resources
(C) Customers
(D) Materials - According to the BCG Matrix, if an SBU of a firm has a low market-share in a high growth market it would be classified as a
(A) Question Mark
(B) Star
(C) Cash Cow
(D) Dog - The control technique ‘PERT’ is an acronym for
(A) Project Evaluation and Review Technique.
(B) Performance Evaluation and ReviewTechnique.
(C) Personnel Evaluation and Review Technique.
(D) Programme Evaluation and Review Technique. 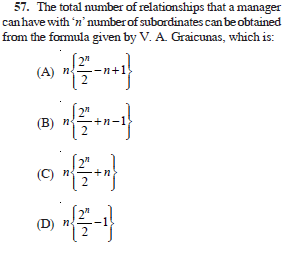
- The ongoing process of systematically indentifying, assessing and developing organisational leadership is known as
(A) Mentoring
(B) Organisational Development
(C) Succession Planning
(D) Career Management - In which of the following performance appraisal technique does the superior keep a log of the positive and negative examples of a subordinate’s work related behaviour?
(A) Forced Distribution Method
(B) Critical Incident Method
(C) Confidential Reports
(D) Paired Comparison Method - Which of the following is not an ‘on-the-job’ training method?
(A) Apprenticeship
(B) Job Rotation
(C) Programmed Instruction
(D) Job Instruction - During the depression, it is advisable to
(A) increase ‘Bank Rate’ and Purchase Securitiesin the open market.
(B) lower ‘Bank Rate’ and Purchase Securitiesin the market.
(C) decrease ‘Bank Rate’ and sell Securities in the open market.
(D) increase ‘Bank Rate’ and sell Securities in the open market. - Read the following statements and give the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) The Banker’s lien is an implied pledge.
(b) Right of lien and right of set-off can be exercised simultaneously at the same time.
(c) One of the essential requirements of a pledge is the actual or constructive delivery of goods pledged by the pawner to the pawnee.
(d) Limitation period for filing a suit for sale of mortgaged property is thirty years from the date of mortgaged debt becoming due.
Codes:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(A) True False False True
(B) True False True False
(C) True True False False
(D) False False True True - Contango charge is paid by a:
(A) Bull Speculator to Bear Speculator
(B) Bear Speculator to Bull Speculator
(C) Stag Speculator to Bull Speculator
(D) Lame Duck to Bear - Match the items of List-I with the items of List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I List-II (a) Debit Card (i) Several Storage (b) Credit Card (ii) Online recovery of amount (c) Electronic Purse (iii) Image Processing use (d) Cheque function (iv) Revolving Credit Codes:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(A) (iii) (i) (iv) (ii)
(B) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(C) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
(D) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i) - Match between types of mutual funds in List-I and their respective features in List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I List-II (a) Open-ended Fund (i) Maximises short-term return to investment. (b) Income Fund (ii) Can sell unlimited number of units (c) Close-ended Fund (iii) The units are not redeemable at their NAV (d) Growth Fund (iv) Maximises long-term return to investors Codes:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(A) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(B) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
(C) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
(D) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv) - The rate at which Bank parks its short-term excess liquidity with RBI is called
(A) Bank Rate
(B) Reverse Bank Rate
(C) Repo Rate
(D) Reverse Repo Rate - Which bank is called the ‘Bank of Issue’?
(A) IFCI
(B) RBI
(C) IDBI
(D) ICICI - Match between List-I (Names of Bank) and List-II (year of establishment) in order to find the correct match using the codes given below the lists:
List-I List-II (a) SBI (i) 1990 (b) SIDBI (ii) 1955 (c) NABARD (iii) 1981 (d) Exim-Bank (iv) 1982 Codes:
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(A) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
(B) (i) (ii) (iv) (iii)
(C) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i)
(D) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii) - For the following statements of Assertion (A) and Reason (R) select the correct code:
Assertion (A) : Banks globally are facing more challenges now, and macro sustainability is a necessity but not sufficient for sustainable economic growth.
Reason (R) : Putting regulation in place is only one part and their implementation is equally important for achieving growth and sustainability.
Codes:
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(C) (A) is true and (R) is false
(D) (A) is false and (R) is true - Which of the following are the instruments of Money Market?
(a) Call Money Market
(b) Commercial Bill Market
(c) Industrial Securities Market
(d) Short-term Loan Market
(e) Treasury Bill Market
Codes:
(A) (a), (b), (c) and (d)
(B) (a), (b), (d) and (e)
(C) (a), (b), (c) and (e)
(D) (a), (c), (d) and (e) - Which of the following examples is not a demographic variable?
(A) Age
(B) Gender
(C) Income
(D) Lifestyle - Skimming price relates to
(A) charging competitive price
(B) charging initially high price
(C) charging initially low price
(D) marginal cost pricing - Which of the following is not a tool of sales promotion?
(A) Sales contests
(B) Free gifts
(C) Point of purchase display
(D) Public relations - Producers of convenience goods typically prefer:
(A) Exclusive distribution
(B) Intensive distribution
(C) Selective distribution
(D) Intermittent distribution - The attempt to build and / or maintain a good “corporate image” is referred to as
(A) Advertising
(B) Publicity
(C) Public Relations
(D) Sales Promotion - The promotional tool which is useful during the decline stage of product life cycle is
(A) Sales promotion
(B) Personal selling
(C) Publicity
(D) Advertising - Which one of the following elements is not in the Marketing Mix of tangible product?
(A) Price
(B) Product
(C) Promotion
(D) Package - Which one of the following is NOT an element of micro-environment of marketing management?
(A) Public
(B) Suppliers
(C) Technological
(D) Competitors - Which of the following is not a characteristic of “Service”?
(A) Intangible
(B) Homogeneous
(C) Perishable
(D) Inseparable - The additional P’s of ‘Service Maketing Mix’ are:
(A) People, Physical evidence, Packaging.
(B) People, Process, Packaging.
(C) People, Physical evidence, Process.
(D) Physical evidence, Process, Packaging. - X entered into contract with Y to deliver certain goods to Y. X offered the goods to Y at proper time and place, but Y refused to accept the goods. In this case
(A) X does not have any right against Y.
(B) X can sue Y for breach of contract, but not discharged from his liability.
(C) X is discharged from his liability and can also sue Y for breach of contract.
(D) Y is not liable for breach of contract. - Problem: M agrees to sell 50 refrigerators to N, at a price to be determined by Z. 30 of 50 refrigerators are delivered to N. N agreed to the above agreement, without asking the
dealer whether the refrigerators are fit to make ice and paid the determined consideration. The refrigerators failed to make ice.
(A) M must refund the price, because refrigerators are meant to make ice.
(B) M will refund the price, only if the buyer would have disclosed the particular purpose.
(C) M will refund the price at this option.
(D) M need not refund the price. - Sec. 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 deals with
(A) Depreciation
(B) Impairment of assets
(C) Liability
(D) CSR - The Negotiable Instruments (Amendment) Bill 2017 inserted a provision allowing a court trying an offence related to cheque bouncing, to direct the drawer (the person who writes the cheque) to pay interim compensation to the complainant. The interim compensation will not exceed ________ per cent of the cheque amount.
(A) 15
(B) 25
(C) 33
(D) 20 - Which of the following will not come under the definition of ‘information’ under RTI Act?
(A) Log books
(B) File notings
(C) Data material held in eletronic form
(D) Circulars - Which of the following is not a cyber crime?
(A) Data theft
(B) Forgery
(C) Damage to data and system
(D) Installing antivirus for protection - In India, the literary work is protected until
(A) life time of author.
(B) 25 years after the death of author.
(C) 40 years after the death of author.
(D) 60 years after the death of author. - Competition Commission of India shall not initiate an inquiry into a combination after the expiry of ________ year(s) from the date on which the combination has taken effect.
(A) one
(B) two
(C) three
(D) five - Goods displayed in a shop with a price label is
(A) an offer
(B) a counter offer
(C) an invitation to offer
(D) a contra offer - The term ‘Goods’ in the Sale of Goods Act means
(A) specific goods only
(B) ascertained goods only
(C) ownership
(D) subject matter - Amitava is an Indian citizen left India for the purpose of employment to USA on 01.08.2018. For the previous year 2018-19 his residential status is:
(A) Resident and ordinarily resident
(B) Resident but not ordinarily resident
(C) Non-resident
(D) Foreigner - Mr. Samanta joined ITC Ltd. as Finance Manager on 01.04.2018. During the year he purchased two residential flats in the same building taking loan from SBI. His annual interest accrued for each flat is Rs. 2,50,000. One of the flats is used for self-occupation and the other one has been let out to a tenant who uses the flat for residential purpose. Mr. Samanta’s total deduction for interest on housing loan is
(A) Rs. 2,00,000
(B) Rs.5,00,000
(C) Rs.2,80,000
(D) Rs.4,50,000 - Mr. Dalmia has one let out property in Kolkata whose Gross Municipal Value is Rs. 4,00,000, Fair Rent is Rs. 4,80,000 and Standard Rent is Rs. 4,50,000. Rent received for 9 month is Rs. 4,14,000 and vacancy period is 3 months. The Gross Annual Value for the Assessment Year 2019-20 is
(A) Rs. 4,14,000
(B) Rs. 4,80,000
(C) Rs.5,52,000
(D) Rs.3,42,000 - Business loss of current year cannot be set off against
(A) House Property Income
(B) Salary Income
(C) Capital Gains
(D) Interest Income - Which of the following income is not an exempted income U/S 10?
(A) Agricultural income in India
(B) Profit from partnership business
(C) Interest from National Savings Certificate(NSC)
(D) Interest from Public Provident Fund (PPF) - Dividend income received during the Previous Year 2018-19 by Mrs. M. Chatterjee is Rs.12,00,000. Tax liability on dividend is
(A) Nil
(B) Rs. 1,00,000
(C) Rs. 20,000
(D) Rs.1,20,000 - Deduction for eligible start-up is available under section
(A) 80IAB
(B) 80IAC
(C) 80IB
(D) 80IBA - Maximum time period to carry forward losses for the activity of owning and maintaining race horses is
(A) 4 years
(B) 8 years
(C) no time limit
(D) cannot carry forward - Share of Agricultural Income and Business Income from growing and manufacturing Tea in India is
(A) 100% Business Income.
(B) 100% Agricultural Income.
(C) 40% Business Income and 60% Agricultural Income.
(D) 60% Business Income and 40% Agricultural Income. - Which of the following is not a Capital Asset?
(A) Self-occupied property in the city of Durgapur
(B) Shares of Indian Company
(C) Jewellery
(D) Personal Car
Answer Key
1 (b) 2 (a) 3 (a) 4 (a) 5 (c) 6 (a) 7 (d) 8 (c) 9 (b) 10 (b) 11 (d) 12 (c) 13 (b) 14 (b) 15 (d) 16 (b) 17 (c) 18 (a) 19 (c) 20 (d) 21 (a) 22 (d) 23 (a) 24 (b) 25 (c) 26 (c) 27 (d) 28 (b) 29 (d) 30 (d) 31 (d) 32 (b) 33 (c) 34 (c) 35 (b) 36 (c) 37 (a) 38 (c) 39 (c) 40 (a) 41 (c) 42 (c) 43 (b) 44 (b) 45 (b) 46 (b) 47 (d) 48 (c) 49 (c) 50 (c) 51 (c) 52 (b) 53 (c) 54 (d) 55 (a) 56 (d) 57 (b) 58 (c) 59 (b) 60 (c) 61 (b) 62 (b) 63 (a) 64 (c) 65 (d) 66 (d) 67 (b) 68 (d) 69 (a) 70 (b) 71 (d) 72 (b) 73 (d) 74 (b) 75 (c) 76 (a) 77 (d) 78 (c) 79 (b) 80 (c) 81 (c) 82 (a) 83 (d) 84 (d) 85 (b) 86 (d) 87 (d) 88 (a) 89 (c) 90 (d) 91 (c) 92 (d) 93 (a) 94 (b) 95 (c) 96 (c) 97 (b) 98 (a) 99 (c) 100 (d)
